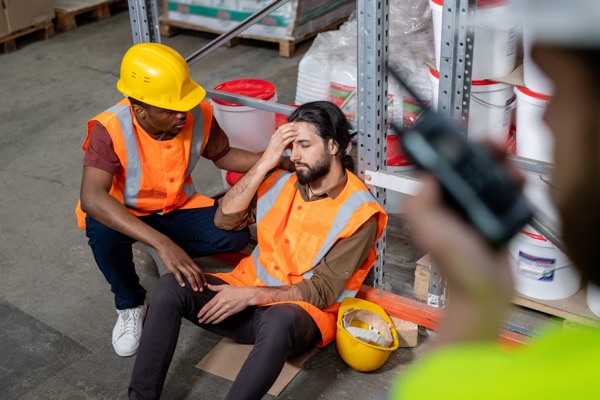
A strong safety culture is the foundation of any successful workplace. When employees are actively engaged in safety practices, the workplace becomes not only compliant but also proactive in preventing accidents and fostering well-being. In 2025, building a safety-first mindset among employees is more critical than ever.
This guide outlines actionable strategies for fostering employee engagement, emphasizing the importance of communication, training, and empowerment to build a robust safety culture.
Why Safety Culture Matters
A safety culture goes beyond policies and procedures. It’s an organizational mindset where safety is a shared value among all employees. When safety is embedded into the workplace ethos, it leads to:
- Fewer Workplace Incidents: A proactive culture reduces hazards and accidents.
- Improved Employee Morale: Employees feel valued and secure when safety is prioritized.
- Increased Productivity: Safe environments lead to less downtime and higher efficiency.
- Enhanced Reputation: A strong safety record positions the company as a responsible employer.
Strategies to Foster a Safety-First Mindset
1. Open and Transparent Communication
Clear communication is the cornerstone of an effective safety culture. Employees need to understand not only the safety protocols but also the rationale behind them.
- Encourage Two-Way Dialogue: Create an environment where employees feel comfortable raising safety concerns without fear of retaliation.
- Leverage Multiple Channels: Use emails, posters, meetings, and digital platforms to share safety updates and reminders.
- Conduct Regular Safety Meetings: Use these meetings to discuss recent incidents, highlight successes, and address emerging risks.
Transparency fosters trust, making employees more likely to participate in safety initiatives.
2. Comprehensive Safety Training
Education is essential to empower employees with the knowledge and skills needed to prioritize safety. Training should be tailored to specific roles and updated regularly to address new challenges.
- Onboarding Programs: Introduce new employees to safety protocols on their first day to set the tone for their engagement.
- Interactive Training: Use hands-on workshops, simulations, and virtual reality to make training sessions engaging and effective.
- Ongoing Learning Opportunities: Schedule refresher courses and advanced training for seasoned employees to reinforce best practices.
Training equips employees to identify hazards and respond effectively, contributing to a safer work environment.
3. Empowering Employees in Hazard Prevention
When employees take ownership of safety, they become active participants in creating a hazard-free workplace.
- Involve Employees in Safety Planning: Invite team members to contribute to safety action plans and risk assessments.
- Assign Safety Champions: Designate employees as safety ambassadors to lead by example and promote best practices.
- Reward Safety Initiatives: Recognize employees who identify hazards, suggest improvements, or consistently follow protocols.
Empowerment fosters accountability, ensuring that everyone plays an active role in maintaining workplace safety.
The Role of Leadership in Building Safety Culture
Leadership commitment is essential for cultivating a safety-first mindset. Managers and supervisors set the tone for workplace behavior, and their actions can inspire employees to prioritize safety.
- Lead by Example: Ensure that leaders consistently follow safety protocols.
- Recognize and Celebrate Success: Highlight milestones and achievements to show that safety efforts are valued.
- Invest in Resources: Provide the necessary tools, equipment, and training to support safety initiatives.
When leadership demonstrates genuine concern for safety, it resonates throughout the organization.
Metrics for Measuring Safety Culture
To ensure progress, companies should track safety performance and use metrics to measure engagement. Consider these indicators:
- Incident Rates: Monitor the number and severity of workplace incidents over time.
- Employee Participation: Track attendance at safety meetings, training sessions, and hazard reporting.
- Safety Audits: Use regular inspections to evaluate adherence to protocols.
- Feedback Surveys: Gather employee input to identify areas for improvement and gauge satisfaction with safety initiatives.
Metrics provide valuable insights and help maintain accountability at all levels.
Continuous Improvement: A Hallmark of Strong Safety Culture
Building a safety culture is an ongoing process. As the workplace evolves, so do its safety challenges. Regularly reassess goals, adapt to emerging risks, and involve employees in continuous improvement efforts.
Tips for Sustaining Momentum:
- Share Success Stories: Celebrate how safety efforts have prevented incidents or improved working conditions.
- Stay Current with Regulations: Ensure compliance with OSHA and other industry standards.
- Encourage Feedback: Continuously solicit and act on employee suggestions.
In 2025, building a stronger safety culture begins with engaging employees at every level. By fostering open communication, investing in comprehensive training, and empowering employees to take ownership of hazard prevention, organizations can create a safer, more productive workplace.
Remember, a safety culture is not built overnight—it requires consistent effort, leadership commitment, and active participation from everyone. Together, let’s make 2025 a year of safety excellence.