Beating the Heat: Essential Strategies for Working Safely in High Temperatures
As summer temperatures rise, so do the risks associated with working in hot environments. Whether you’re employed in construction, landscaping, agriculture, or any other outdoor occupation, understanding how to beat the heat is crucial for your health and safety. This blog provides essential strategies to help you stay safe and productive when the mercury climbs.
Understanding Heat-Related Illnesses
Before diving into prevention strategies, it’s important to understand the types of heat-related illnesses that can affect workers:
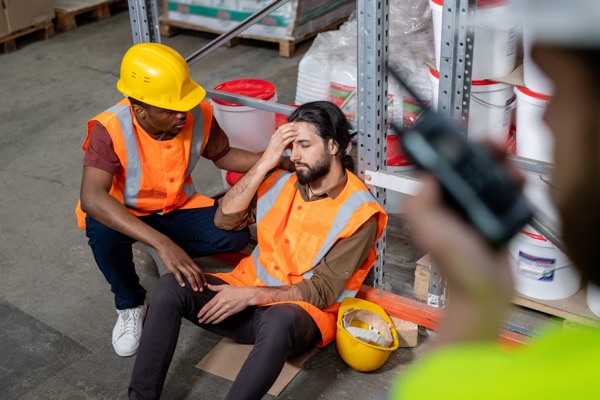
- Heat Stroke: The most severe form of heat illness, characterized by a high body temperature (104°F or higher), confusion, loss of consciousness, and potential organ failure. It requires immediate medical attention.
- Heat Exhaustion: Symptoms include heavy sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and headache. It’s a precursor to heat stroke and should be treated promptly.
- Heat Cramps: Muscle spasms caused by the loss of salts and electrolytes through sweating. These can be painful and typically occur during or after intense physical activity.
- Heat Rash: Skin irritation from excessive sweating, commonly seen in hot, humid conditions.
Key Strategies for Staying Safe
1. Hydration is Crucial
Staying hydrated is the most important step in preventing heat-related illnesses. Drink water frequently, even if you don’t feel thirsty. Aim for at least one cup every 15-20 minutes. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, as they can contribute to dehydration.
2. Take Regular Breaks
Scheduling regular breaks in shaded or air-conditioned areas can significantly reduce the risk of heat exhaustion and heat stroke. Employers should provide rest breaks and encourage workers to use them, especially during the hottest parts of the day.
3. Wear Appropriate Clothing
Lightweight, loose-fitting, and light-colored clothing helps reflect heat and allows for better air circulation. Protective gear, such as wide-brimmed hats and UV-protective sunglasses, can also help shield workers from direct sun exposure.
4. Use Sunscreen
Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher can protect the skin from harmful UV rays. Reapply every two hours, or more often if sweating heavily.
5. Implement a Heat Acclimatization Program
Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of work in hot conditions allows the body to adapt to the heat. This process, known as acclimatization, can take up to two weeks and significantly improves the body’s ability to cope with high temperatures.
6. Monitor Workers’ Health
Supervisors should be trained to recognize the symptoms of heat-related illnesses and act quickly if they occur. Implementing a buddy system where workers monitor each other’s condition can also be effective.
7. Adjust Work Schedules
When possible, schedule the most strenuous tasks for the cooler parts of the day, such as early morning or late afternoon. Reducing physical exertion during peak heat hours can help prevent overheating.
8. Provide Cooling Solutions
Fans, misting stations, and portable air conditioners can help reduce heat exposure. Cooling vests and bandanas can also provide relief for workers in extremely hot conditions.
The Role of Employers
Employers play a critical role in ensuring a safe working environment. This includes providing adequate water, rest breaks, and shade, as well as training employees on the risks of heat-related illnesses and the measures to prevent them. Creating a comprehensive heat illness prevention plan and ensuring compliance with occupational safety guidelines is essential.
Conclusion
Working in high temperatures poses significant risks, but with the right strategies and precautions, these risks can be managed effectively. By staying hydrated, taking regular breaks, wearing appropriate clothing, and being aware of the signs of heat-related illnesses, workers can stay safe and productive throughout the hot summer months. Employers must also do their part to provide a safe working environment and educate their workforce on the importance of heat safety.